The Power of AI to Defeat Phishing
by Josh Lamb on Oct 8, 2018 12:00:00 AM
An average of 126,000 domain names are registered every single day¹. Some of these can be registered for less than $1 USD and used to launch any number of phishing campaigns on unsuspecting users. An attacker can quickly copy over legitimate logos, diagrams, and graphics from trusted companies and easily create fake forms to capture user passwords and sensitive data. By the time someone spots and reports the abuse, the attacks have long since vanished.
This creates a problem for companies that rely on human-generated blocklists. The lag-time associated with human reporting means they will never be able to respond quickly enough to this type of attack. Whether the list is crowd-sourced or managed by a professional security company, it shares the same fatal flaw, phishing sites won’t be blocked until they are reported and added to a list. Are there any better alternatives?
The past five years have seen a dramatic increase in the use of Artificial Intelligence. Most people may not realize that AI already empowers their questions to Siri, the spam-blocker for their email account, their Facebook newsfeed, and their conversations with technical support. Behind the scenes, AI is churning through the 2.5 quintillion bytes of data that is generated each day and turning it into useful information².
This is also a game changer for internet security. AI can crawl through web domains and make instantaneous and highly accurate categorizations of content, in a manner that is orders of magnitude faster and with more depth than a human being. When it comes to combating phishing, AI is able to meet the challenge by scanning sites in real-time and determining if they belong to trusted entities or not. One of the way to do this is through image recognition. AI compares copied or slightly-altered images on a website, to that of trusted entities and can spot even minute differences. It can also compare this with many other data points (website copy, DNS records, etc) to assess and score a newly seen or newly registered domain. This opens the possibility to shift the security timeline from reactive to proactive — intercepting an attack that has not yet been launched.
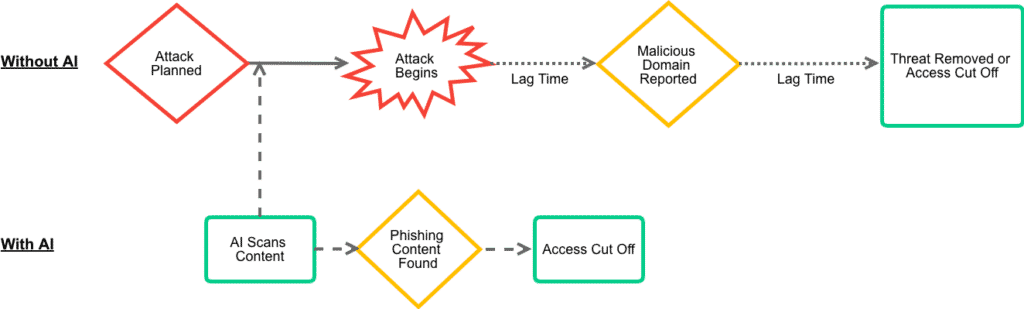
DNSFilter uses our AI engine to scan newly registered domains for phishing threats and to categorize the content of sites into their appropriate categories. If a website has never been viewed by our customers, our engine can scan it in real-time and block/allow access based on this categorization, all within 60 seconds. We believe AI is the future of internet security, and the way to shift security from being reactive, to proactive.
[1]: Whoisds (September 17, 2018). Newly Registered Domains https://whoisds.com/newly-registered-domains
[2]: Forbes. How much data do we create every day? https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2018/05/21/how-much-data-do-we-create-every-day-the-mind-blowing-stats-everyone-should-read
 The Big Game, Olympic Mania: Navigating the Surge in Malicious Sports Betting Sites
The Big Game, Olympic Mania: Navigating the Surge in Malicious Sports Betting Sites
With the Super Bowl and 2026 Winter Olympics coinciding, all eyes have been on the world of sports in February. And with that comes some unfortunate realities: Scammers take advantage of seasonal events like this every way they can.
 6 Security-Focused New Year’s Resolutions for 2026
6 Security-Focused New Year’s Resolutions for 2026
The start of a new year is the perfect time to reset habits—not just personal ones, but digital habits too. Cybercriminals don’t need zero-days or nation-state tooling if we keep handing them easy wins through reused passwords, oversharing, and rushed reactions.

