Say Hello to SSO on DNSFilter
by Aliese Alter on Apr 10, 2022 12:00:00 AM
What is SSO?
Single Sign-On is an authentication protocol that allows users to sign into different software systems using a single identity. This identity is provided by third-party identity providers like Okta, OneLogin, or Azure AD.
The application you’re trying to authenticate with sets up a trust relationship with the identity provider that already has your authentication credentials. A certificate shared by the identity platform and the software you’re trying to access is used to sign identity information being shared by the two systems.
This allows you to use your credentials that have been saved on the identity provider to securely access the software. Below is a diagram that details how SSO works:
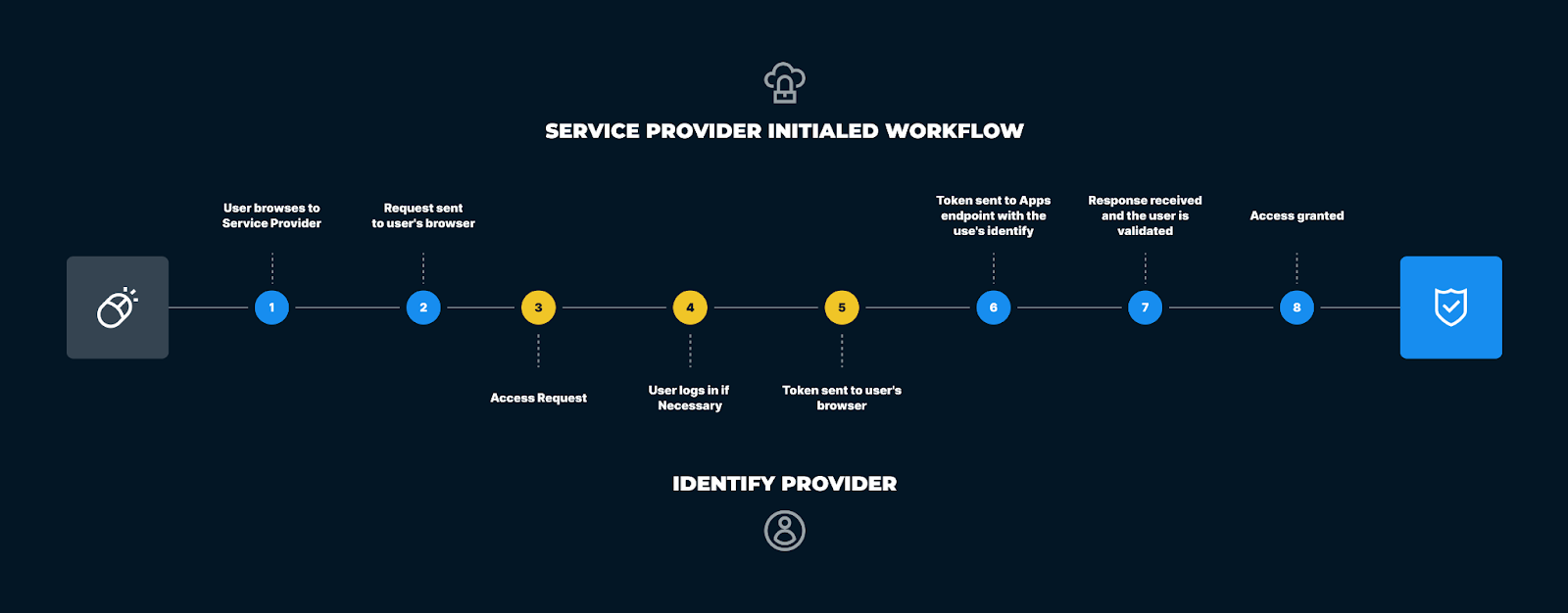
SSO on DNSFilter
DNSFilter customers can now configure Single Sign-On (SSO), enabling dashboard users to securely authenticate with the DNSFilter application.
DNSFilter already makes both threat protection and content filtering easy and affordable. SSO configuration is no different. Customers can optionally control who has access to the DNSFilter application using any Identity Provider (IdP) that supports Generic OpenID (OIDC) protocol, such as Okta and Microsoft Azure Active Directory. DNSFilter has no plans to be featured on the SSO Wall of Shame; so SSO will be offered free of charge to all plans.
How to get started with SSO on DNSFilter
SSO can be configured through the DNSFilter dashboard. Account owners can simply enter their OAuth 2.0 credentials from an IdP in the Single Sign-On section of the Settings page of their DNSFilter account. Once the values have been entered correctly, SSO can be turned on.
For more information on setting up Single Sign-On on your DNSFilter account, checkout the detailed guide on our knowledgebase.
Take advantage of this new functionality today!
 6 Security-Focused New Year’s Resolutions for 2026
6 Security-Focused New Year’s Resolutions for 2026
The start of a new year is the perfect time to reset habits—not just personal ones, but digital habits too. Cybercriminals don’t need zero-days or nation-state tooling if we keep handing them easy wins through reused passwords, oversharing, and rushed reactions.
 Inside Business Email Compromise Scams: How to Protect Your Business
Inside Business Email Compromise Scams: How to Protect Your Business
The Scam That Outsmarts Awareness Training
It starts with a routine email.



